Accounting Basics
What is an Accounting?
Accounting is used for business entities and it is a systematic process of identifying, recording of financial transactions, and it also indicates the process of summarizing, analyzing, and presenting various financial reports of a business.
Business owners would like to know the financial status of the business and they can see the financial status by preparing of business financial reports like trail balance, profit & loss account and balance sheet.

Accounting Concepts
The following are the important accounting concepts
Business Entity Concept
According to the business entity concept, transactions are associated with business and owner of the business are two different entities.
All business transactions are treated and accounted for separately from the personal transactions of its owner.
Money Measurement Concept
According to this concept, only business transactions which can be measured in terms of money recorded in accounting.
Example
Purchased 2 HP computers each@ Rs.20,000 and purchased 4 Samsung mobile phones.
You can record only HP computers transaction in your books of accounts with the value of Rs.40,000, because this transaction measured in terms of money.
Going Concern Concept
According to going concern concept, the business entity can continue its operations long time and the business will not liquidate or be forced to discontinue its operations due to any reason.
Cost Concept
It is also known as historical cost concept and it indicates that the original cost of an asset is recorded in company’s books of accounts not on the market value of the asset.
Example, ABC company purchased land 5 years ago for Rs.2,00,000 and the same has been recorded in its accounting records. The current market value of land is Rs.3,00,000, the amount shown in the balance sheet and other accounting records would continue with the unchanged cost of Rs.2,00,000.
Matching Concept
This is one of the accounting concepts, it indicates that you have to match revenues and their related expenses in same accounting period and this gives the net profit earned in particular accounting period.
Accrual Concept
This is also known as the mercantile system of accounting. The expenses and revenues that have been incurred or earned during the month, but will be paid or received in the future has to be recorded in the books of accounts as per accrual base system of accounting.
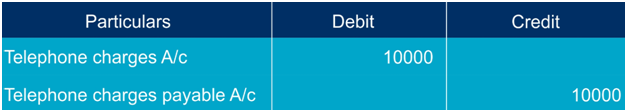
Example: Telephone charges incurred for April is Rs.10,000 but the due date is 10th of the following month (May), in this case you have to make telephone charges provision entry at April month end.
Dual Aspects Concept
It indicates that every business transaction as two aspects, one is giving aspect and another one is receiving concept. In every transaction there must be two accounts involved one account is debit and another one credit
Example: started business with sum of Rs.50,000 then record the below entry
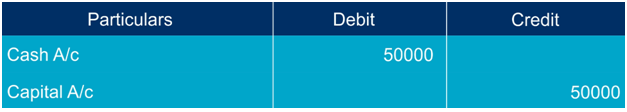
Give the cash account to debit because it is coming into the business and business owner is investing (giving) money as a capital, so credit the capital account.
The capital value of the business is equal to the assets value of the business.
So, the dual aspect concept indicates that Capital + Liabilities = Assets.
Accounting Period Concept
This accounting period concept refers that for which period the financial statements are prepared for internal and external reporting purpose. Generally, the accounting period is 12 months, but the beginning and ending of the financial year is different based on the country.
Accounting Rules of Debit & Credit
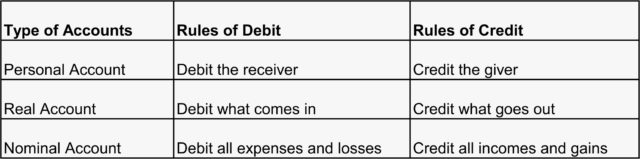
Classification of accounts
You should understand the classification of accounts and their treatment in double entry system of accounting. The accounts are classified into three categories.
1.Personal Accounts
2.Real Accounts
3.Nominal Accounts
1. Personal Accounts
An account associated with any individual and artificial person like, Ram, Peter, Johan, M/s. XYZ Ltd and Johan Industries is called as a personal account.
Example: Bank, John& co, capital and debitors
2. Real Accounts
Accounts are related Assets and Properties is called a real account.
Tangible assets
Where you can see and touch the assets called Tangible assets.
Example: building, plant & machinery and furniture
Intangible Assets
Where you cannot see and touch the assets called Intangible assets.
Example: Goodwill, trademarks & copyrights etc.
3. Nominal Accounts
Those accounts are related to Income, Expenses, losses and gains called nominal accounts.
Example: Wages account, rent account, interest account, salary account and revenue account other income accounts.
Related Topics
Discount Allowed and Discount Received
Related Pages
- Fixed Asset Entries
- Payroll Journal Entries
- Accrued Expenses
- Prepaid Income
- Debits and Credits
- Chart of Accounts
- Bookkeeping
- Petty Cash
- Bank Reconciliation
- Accounts Payable Process
- Accounts Receivable Process
- Prepaid Expenses
- Discount Allowed and Discount Received
- Journal Entries
- Adjusting Entries
- Depreciation
- Current Liabilities and Current Assets